The Cryptocurrency Market Is Growing Exponentially
Bitcoin dominates over other digital currencies today, but the data suggests its market share will drop significantly in the next few years.
When it comes to the future of money, there is a growing consensus that cryptocurrencies are set to play a major role. One cryptocurrency, in particular, has entered the public lexicon as the go-to digital asset: Bitcoin.
But the cryptocurrency market is significantly more complex than the public lexicon might suggest. And while there have been plenty of studies examining the role and future of Bitcoin, there have been few that explore the broader cryptocurrency market and how it is evolving.
Today that changes thanks to the work of Abeer ElBahrawy at City University in London and a few pals who have examined the cryptocurrency market as a whole and say that it is significantly more complex and mature than many had thought. The evolution of this market even bears a remarkable similarity to the evolution of ecosystems in many other areas, providing some insight into the way the cryptocurrency market might change in the future.
First some background. The big challenge with digital currency is to prevent unauthorized copying. Cryptocurrencies use two mechanisms to prevent this. The first is to publish every transaction in a public record and to store numerous copies of this ledger online in a way that allows them all to be automatically compared and updated. This prevents double spending—using the same bitcoin to buy two different things.
The second mechanism is to protect the ledger cryptographically. Every update collects together a range of new transactions and adds them to the existing ledger. But to do this, the earlier version of the ledger is first frozen and encrypted.
The new version of the ledger—called a block—includes the encrypted copy of the earlier ledger. Anybody can use this encrypted data to generate a number that can be used to check the veracity of the block. However, it is extremely hard to generate this number computationally in an attempt to game the system. It is this feature—that the blocks are easy to check but extremely hard to copy—that secures the system.
Of course, as the ledger continues to be updated, new blocks must be created, piggybacking on the old ones and creating an unbroken chain of blocks. Hence, the term blockchain technology.
Bitcoin is by far the most famous of these cryptocurrencies. It is also among the oldest, having first emerged in 2009. But it is by no means the only cryptocurrency. So an interesting question is how the cryptocurrency market is evolving.
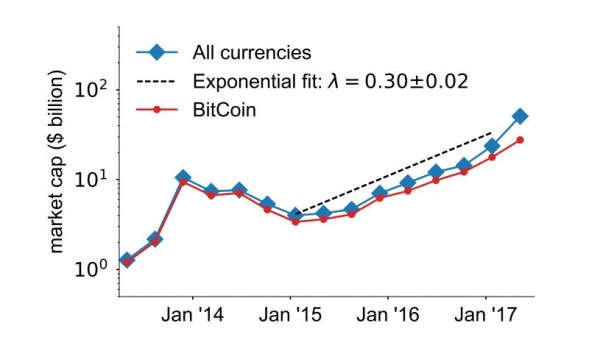
To find out, ElBahrawy and co analyzed the behavior of 1,500 cryptocurrencies that have emerged since 2013 and say that some 600 of them are actively traded today. They say this market has recently entered a period of exponential growth and is currently worth $54 billion. (By comparison, the total amount of money in the world is about $60 trillion.)
But while this cryptocurrency market is growing rapidly, ElBahrawy and co show that certain aspects of it are stable. For example, the number of active cryptocurrencies has remained about the same since 2013 as has the market share distribution, which follows a well-known power law.
The team also shows how this distribution can be reproduced using a standard model of evolution in which they plug in figures for the rate at which currencies emerge and die away.
This power law distribution occurs in a wide range of systems. For example, the same law describes the size of religions, of languages and even of wars (by number of deaths). In none of these systems is there are any favored religion or language or war. But all things being equal, they all form this type of distribution.
The fact that size distribution of cryptocurrencies follows the same law is significant. It implies that as far as the market is concerned, all currencies are essentially the same. “The fit with the data shows that there is no detectable population-level consensus on what is the ‘best’ currency or that different currencies are advantageous for different uses,” say ElBahrawy and co.
Whether that is true is up for debate. Various critics have pointed out a number of technical limitations associated with Bitcoin, and this has inspired a new generation of cryptocurrencies, such as Ethereum. Whether this will influence the market remains to be seen.
While this exponential growth is ongoing, Bitcoin’s market share is falling. The top five biggest currencies—Ethereum, Ripple, Litecoin, Dash, and Monero—now account for 20 percent of the market. And the trend for Bitcoin is clear. “This would predict Bitcoin market share to fluctuate around 50 percent by 2025,” say the team.
Another factor in the market is that cryptocurrencies aren’t used only as currency. Bitcoin is also widely used for speculation and can also be used for nonmonetary uses such as timestamping.
For many of these applications there is a clear benefit to having a single currency that everyone agrees on. “While the use of cryptocurrencies as speculative assets should promote diversification, their adoption as payment method (i.e., the conventional use of a shared medium of payment) should incentivize a winner-take-all regime,” say Bickell and co.
But experience with other ecosystems suggest that this is by no means certain to happen. For example, a single computer operating system has never been able to outcompete all others, regardless of the ruthlessness of its deployment. Neither has any human language or religion or fashion wiped out all others.
That’s not to say it can’t happen. But unless there is significant external manipulation of this market, the likelihood is that there will be significant diversity in the cryptocurrency market for the foreseeable future.
David Ogden
Entrepreneur
David